
DGPS stands for Differential Global Positioning System. DGPS enhances the standard Global Positioning System (GPS) by correcting errors in GPS signals caused by factors such as atmospheric interference and clock inaccuracies, thereby improving location accuracy. DGPS surveying is useful for infrastructure projects including utility installations and road development. Precise location information guarantees accurate construction operations, reducing mistakes and rework. This is especially important for urban planning, as new infrastructure must fit in with the rules and institutions already in place.
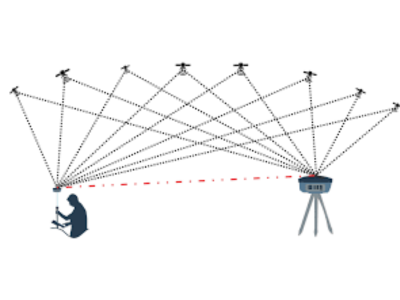
DGPS operates by comparing the GPS signals received by a stationary reference station with its known position and then transmitting correction data to nearby DGPS-enabled receivers. This correction data allows DGPS receivers to determine their positions with significantly higher accuracy, typically within a few meters.
DGPS has two receivers namely the Reference Receiver and the Rover Receiver. The pseudo ranges received by the reference receiver as in any GPS are corrected by the actual ranges received by the rover receiver. Unlike GPS, DGPS does not have a global range. It is localized and its range has local coordinates. This property of the DGPS makes it more accurate and expensive as it caters only to the local requirements.
A DGPS machine enhances standard GPS accuracy by correcting signal errors. DGPS machine components typically includes a stationary reference station and mobile DGPS-enabled receivers. DGPS machine functionality helps correct atmospheric errors, satellite orbit, and clock errors to provide precise location data, improving accuracy from several meters to within a few centimeters.
